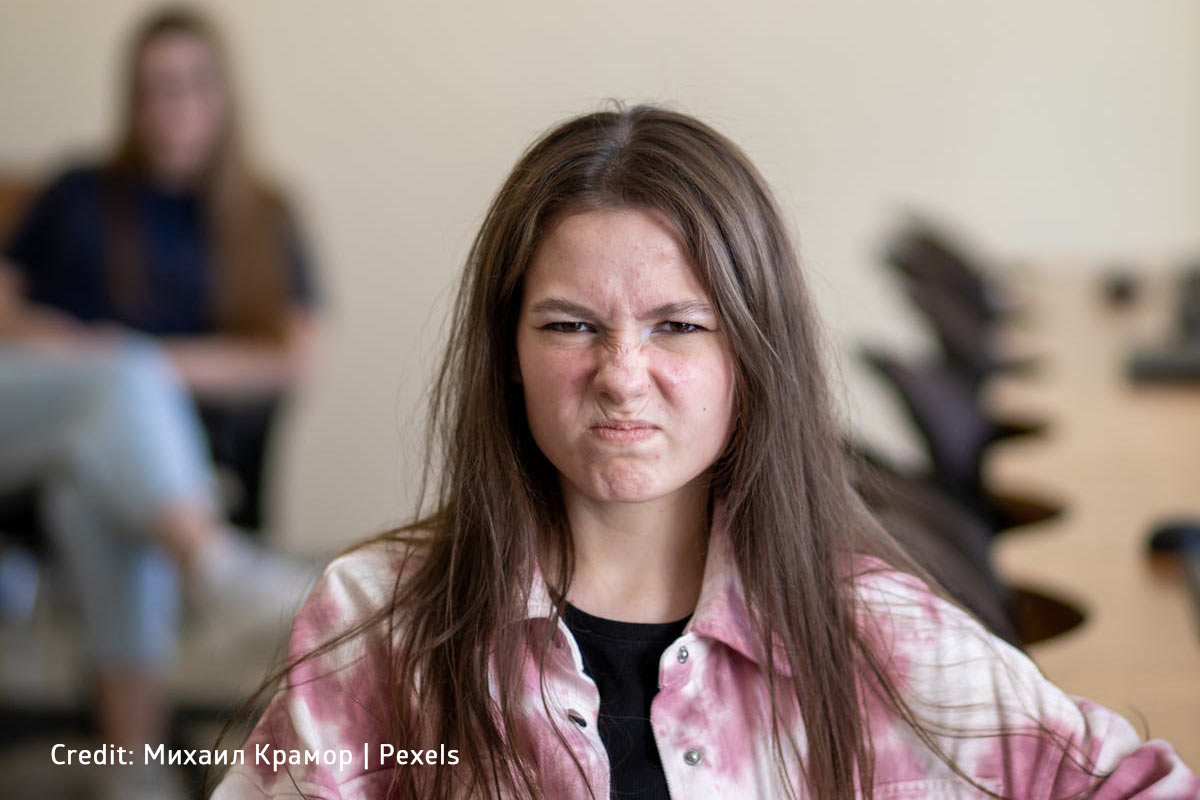
Anger is a normal human emotion. However, when it becomes overwhelming and uncontrollable, it can lead to significant problems for teens and those around them. Understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and learning effective coping techniques can help teens manage their anger healthily.
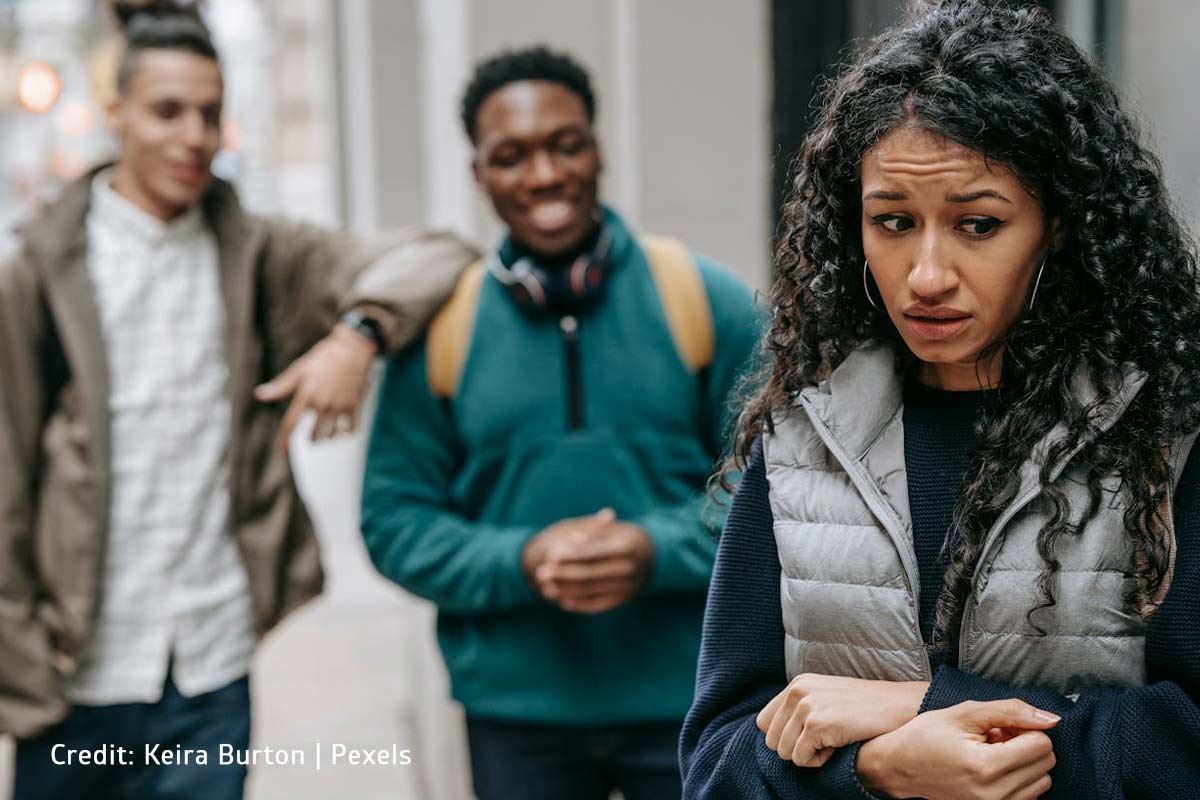

Causes of Teen Anger
Several factors can contribute to teen anger:
Hormonal Changes
Adolescence is a period of significant hormonal shifts. Fluctuating levels of hormones like testosterone and estrogen can intensify emotions, making teens more susceptible to mood swings, irritability, and anger. These hormonal changes can amplify reactions to stress, frustration, and perceived slights.
Stress and Pressure
- Academic Stress: The pressure to achieve good grades, meet deadlines, and excel in standardized tests can be overwhelming.
- Peer Pressure: The desire to fit in and be accepted by peers can lead to anxiety, insecurity, and anger when expectations aren’t met. While not all peer pressure is bad, KidsHealth.org says that “[Peers] may pressure [teens] into doing something [they’re] uncomfortable with, such as shoplifting, doing drugs or drinking, taking dangerous risks when driving a car, or having sex before [they] feel ready.”
- Family Conflict: Family tension, arguments, or inconsistent parenting can create a stressful environment that triggers anger.
Lack of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and manage emotions, is still developing in adolescents. When teens struggle to identify and express their feelings healthily, they may resort to anger as a default response. This can lead to impulsive outbursts and difficulty resolving conflicts.
Mental Health Conditions
Underlying mental health conditions can significantly contribute to teenage anger.
- Anxiety: Constant worry and fear can manifest as irritability and aggression.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness can lead to frustration and anger.
- ADHD: Difficulty focusing, impulsive behaviour, and hyperactivity can trigger anger and frustration.
Substance Abuse
Alcohol and drug use can exacerbate anger issues in several ways:
- Impaired Judgment: Substance abuse can cloud judgment, leading to impulsive and aggressive behaviour.
- Increased Sensitivity: Substance use can heighten emotional responses, making teens more prone to anger.
- Mask Underlying Issues: Substance abuse may be a way to cope with underlying mental health conditions or emotional pain, leading to increased anger.
The Effects of Teen Anger
Uncontrolled teen anger can have significant negative impacts on various aspects of a young person’s life. Here are some of the potential consequences:
Personal Consequences
- Damaged Self-Esteem: Frequent outbursts and negative self-talk can erode self-worth and confidence.
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Chronic anger can lead to heightened stress levels and anxiety, affecting overall well-being.
- Physical Health Problems: Anger can contribute to physical health issues such as headaches, stomachaches, and high blood pressure.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep can result from racing thoughts and emotional turmoil.
Interpersonal Consequences
- Strained Relationships: Angry outbursts can damage relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners.
- Social Isolation: Fear of rejection or conflict may lead to withdrawal from social activities and isolation.
- Conflict with Authority Figures: Difficulty respecting authority figures, such as teachers or parents, can lead to disciplinary problems.
Academic Consequences
- Poor Academic Performance: Anger can disrupt concentration, focus, and motivation, leading to lower grades and academic difficulties.
- Behavioural Problems: Anger outbursts in school can lead to disciplinary actions and negative interactions with peers and teachers.
Long-Term Consequences
- Substance Abuse: As a coping mechanism, teens may turn to alcohol or drugs to self-medicate and numb emotional pain.
- Legal Trouble: Uncontrolled anger can lead to impulsive actions that may result in legal consequences.
- Mental Health Issues: Chronic anger can contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or personality disorders.
Signs of Teen Anger
Recognizing the signs of teen anger can help parents and caregivers intervene early. Some common signs include:
- Frequent Outbursts: Frequent tantrums, yelling, or physical aggression.
- Withdrawn Behavior: Isolating oneself, avoiding social interactions, or withdrawing from hobbies.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Struggling to focus on tasks or schoolwork.
- Physical Symptoms: Headaches, stomachaches, or other physical complaints.
- Risk-Taking Behavior: Engaging in reckless or dangerous activities.
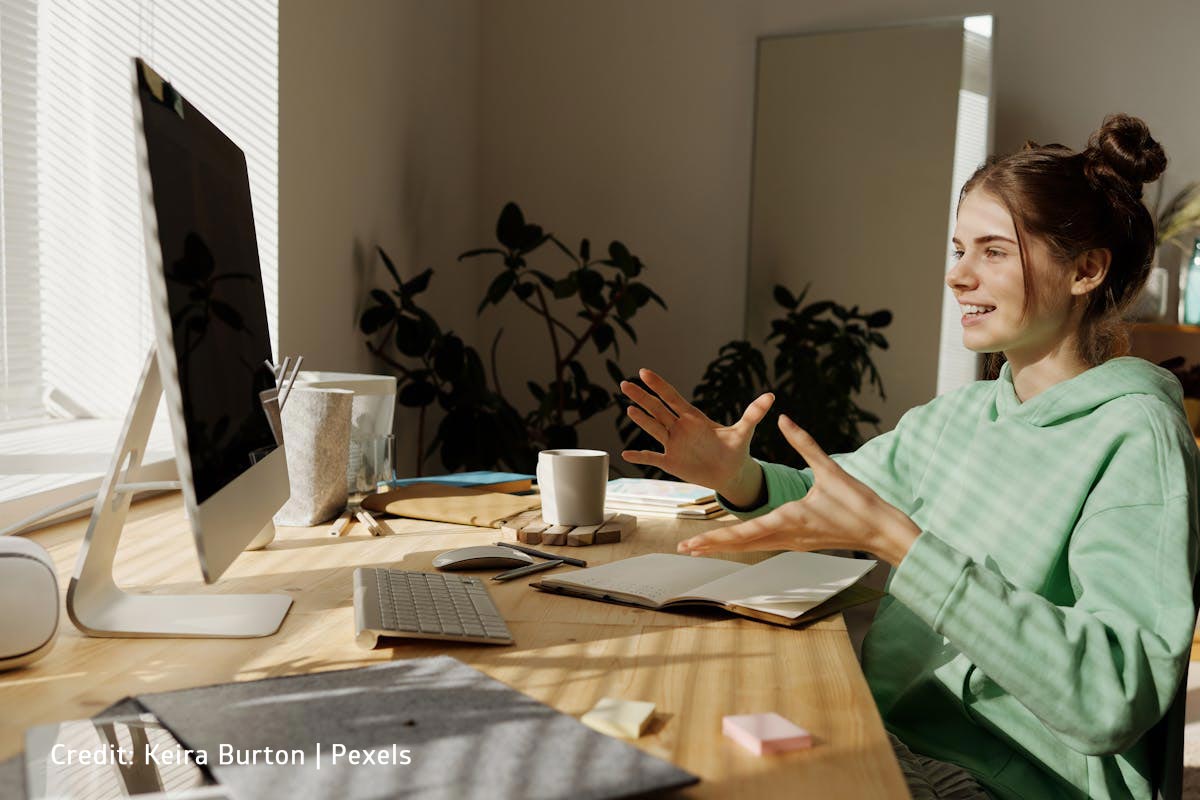

Effective Coping Techniques for Teen Anger
If you or your teen is struggling with anger, there are several effective coping techniques to try:
Mind-Body Techniques
- Deep Breathing: This simple yet powerful technique involves taking slow, deep breaths, focusing on the sensation of the breath entering and leaving the body. It can help calm the nervous system and reduce feelings of anxiety and anger.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, can help teens become more aware of their thoughts and emotions. By observing their feelings without judgment, they can learn to regulate their responses to stress and anger triggers.
Physical Outlets
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as sports, dancing, or running, can help release pent-up energy and reduce stress hormones. Exercise can also boost mood and improve overall well-being.
- Time-Out: Taking a short break from a stressful situation can help prevent impulsive reactions. A time-out can involve going to a quiet room, taking a walk, or listening to calming music.
Seeking Professional Help
If teen anger is severe or persistent, seeking professional help is a necessity. A Barrie therapist can provide personalized guidance and support, such as:
- Individual Therapy: One-on-one therapy sessions can help teens explore the underlying causes of their anger and develop effective coping strategies.
- Family Therapy: Family therapy can help improve communication and resolve family conflicts that may be contributing to teen anger.
- Group Therapy: Group therapy provides a supportive environment where teens can share their experiences, learn from others, and develop social skills.
Seeking Professional Help
If your teen’s anger is significantly impacting their life or the lives of others, seeking professional help is essential. A therapist can provide specialized tools and techniques to help teens manage their anger effectively.
Additional Tips for Parents and Caregivers
- Set Clear Expectations: Establish clear rules and consequences for inappropriate behaviour.
- Active Listening: Listen attentively to your teen’s concerns and feelings.
- Validate Emotions: Acknowledge your teen’s feelings without judgment.
- Model Healthy Behaviour: Demonstrate healthy ways of expressing emotions.
- Encourage Positive Relationships: Support your teen’s friendships and social activities.
By understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and implementing effective coping techniques, teens can learn to manage their anger healthily and lead fulfilling lives. If you or your teen needs additional support, don’t hesitate to seek professional help.
Reach out to Insight Centre Counselling & Psychotherapy at +1 647-633-1928. We offer a range of services, including teen therapy, family therapy, and group therapy, to address various mental health concerns, including anger management.